Call a Smart Contract
Introduction
In this section, we will guide you through the creation of an application that will call a smart contract to read and write.
Tutorial Prerequisites
Before starting, make sure you have gone through the prerequisites.
Receive Ether token in your Ledger Nano Ethereum Sepolia account
- Create an Ethereum Sepolia account in Ledger Live
- Send Sepolia Eth to your account with Infura faucet (opens in a new tab). You will need to create an account that will be useful later for the API key.
 Fig. 1: Sepolia Ethereum Faucet
Fig. 1: Sepolia Ethereum Faucet
Web App Bluetooth (only Nano X)
The Ledger Nano S and S Plus do not have the Bluetooth functionality. This tutorial will only work with a Ledger Nano X.
Please be aware that the Bluetooth implementation is only supported by a few browsers. You can check the browser support (opens in a new tab) for the Web Bluetooth transport.
Project Initialization
The app is build with React, which is a frontend Javascript framework.
First, open a terminal and create a new project. For this tutorial the project will be named "e2e-tutorial-contract". Run:
npx create-react-app e2e-tutorial-contract
cd e2e-tutorial-contractOpen the folder in an text editor.
Run:
mkdir pages
mkdir styles
touch ./ConnectLedger.js
touch ./SmartContract.js
touch ./ethereum.js
touch ./styles/global.css
touch ./styles/Home.module.css
mv src/index.js pages
mv src/App.js ./
rm -r src The folder will contain these files:
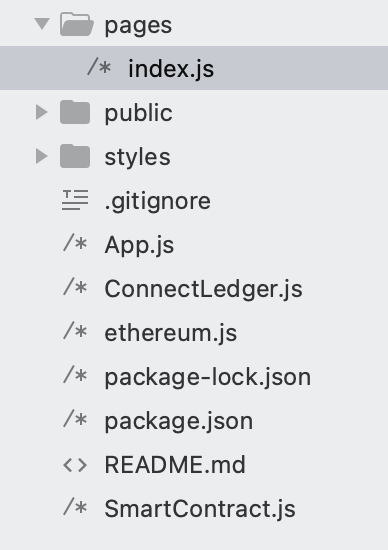 Fig. 1: Folder of the Application
Fig. 1: Folder of the Application
To implement the Ledger connexion you will only modify "App.js", "index.js", "ConnectLedger.js”,"SmartContract.js", and ethereum.js”
Code Implementation
App.js
In App.js copy-paste the following code:
import React, { useState } from 'react';
import ConnectLedger from './ConnectLedger.js';
import SmartContract from './SmartContract.js';
function App() {
const [transport, setTransport] = useState(undefined);
const [eth, setEth] = useState(undefined);
const [address, setAddress] = useState(undefined);
const saveInfo = (info) => {
setAddress(info.address);
setEth(info.eth);
setTransport(info.transport);
}
return (
<div className='container'>
{
!transport ?
<ConnectLedger onTransport={(info) => saveInfo(info)}></ConnectLedger> :
<SmartContract address={address} eth={eth}></SmartContract>
}
</div>
);
}
export default App;ConnectLedger.js
In ConnectLedger.js, copy-paste the following code:
import React from 'react';
import TransportWebBLE from "@ledgerhq/hw-transport-web-ble";
import Eth from "@ledgerhq/hw-app-eth";
function ConnectLedger({onTransport}) {
const connectLedger = async() => {
const transport = await TransportWebBLE.create();
const eth = new Eth(transport);
const {address} = await eth.getAddress("44'/60'/0'/0/0", false);
onTransport({address,eth,transport})
}
return (
<div className='container'>
<div className='row'>
<div className='col-sm-4 mt-5 mx-auto'>
<button onClick={connectLedger}>Connect Your Ledger</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
);
}
export default ConnectLedger;SmartContract.js
In "SmartContract.js", copy-paste the following code and replace {YOUR_INFURA_APIKEY} by the API key you will find on your Infura account:
import React, { useState } from 'react';
import getBlockchain from './ethereum.js';
import { ethers } from 'ethers';
import { ledgerService } from '@ledgerhq/hw-app-eth'
function SmartContract({eth,address}) {
const [simpleStorage, setSimpleStorage] = useState(undefined);
const [data, setData] = useState(undefined);
const [provider, setProvider] = useState(undefined);
const [url, setUrl] = useState(undefined);
const smartContractRead = async() => {
const provider = new ethers.providers.JsonRpcProvider('https://sepolia.infura.io/v3/{YOUR_INFURA_APIKEY}');
const { simpleStorage } = await getBlockchain(provider);
console.log(simpleStorage);
const data = await simpleStorage.readData();
setProvider(provider);
setSimpleStorage(simpleStorage);
setData(data);
};
const updateData = async e => {
e.preventDefault();
const dataInput = e.target.elements[0].value;
console.log(simpleStorage);
const { data } = await simpleStorage.populateTransaction['updateData(uint256)'](dataInput);
const unsignedTx = {
to: simpleStorage.address,
gasPrice: (await provider.getGasPrice())._hex,
gasLimit: ethers.utils.hexlify(100000),
nonce: await provider.getTransactionCount(address, "latest"),
chainId: 11155111,
data: data,
}
console.log(unsignedTx);
const defaultLoadConfig = {
nftExplorerBaseURL: "https://nft.api.live.ledger.com/v1/ethereum",
pluginBaseURL: "https://cdn.live.ledger.com",
extraPlugins: null,
cryptoassetsBaseURL: "https://cdn.live.ledger.com/cryptoassets"
};
const serializedTx = ethers.utils.serializeTransaction(unsignedTx).slice(2);
const resolution = await ledgerService.resolveTransaction(serializedTx, defaultLoadConfig, {});
console.log(serializedTx);
const signature = await eth.signTransaction(
"44'/60'/0'/0/0",
serializedTx,
resolution
);
console.log(signature);
//Parse the signature
signature.r = "0x"+signature.r;
signature.s = "0x"+signature.s;
signature.v = parseInt("0x"+signature.v);
signature.from = address;
console.log(signature);
//Serialize the same transaction as before, but adding the signature on it
const signedTx = ethers.utils.serializeTransaction(unsignedTx, signature);
console.log(signedTx);
const hash = (await provider.sendTransaction(signedTx)).hash;
console.log(hash);
setUrl("https://sepolia.etherscan.io/tx/" + hash);
};
return (
<div className='container'>
<div className='row'>
<div className='col-sm-4'>
<h2>Data:</h2>
<p>{data ? data.toString() : "..." }</p>
<button onClick={() => smartContractRead()}>Get Data</button>
</div>
<div className='col-sm-4'>
<h2>Change data</h2>
<form className="form-inline" onSubmit={e => updateData(e)}>
<input
type="text"
className="form-control"
placeholder="data"
/>
<button
type="submit"
className="btn btn-primary"
>
Submit
</button>
</form>
</div>
<div className="mt-5 mx-auto d-flex flex-column">
<p>
Sepolia Etherscan :
</p>
<p><a href={url} target="_blank" rel="noreferrer">{url}</a></p>
</div>
</div>
</div>
);
}
export default SmartContract;ethereum.js
In "ethereum.js", copy-paste the following code:
import { Contract } from 'ethers';
const getBlockchain = (provider) =>
new Promise( async (resolve, reject) => {
if(provider) {
const simpleStorage = new Contract(
"0xA0aB0fae9C6b4882dC3690cb1705D5Aeb8c436d7",
[
{
"inputs": [],
"name": "data",
"outputs": [
{
"internalType": "uint256",
"name": "",
"type": "uint256"
}
],
"stateMutability": "view",
"type": "function"
},
{
"inputs": [],
"name": "readData",
"outputs": [
{
"internalType": "uint256",
"name": "",
"type": "uint256"
}
],
"stateMutability": "view",
"type": "function"
},
{
"inputs": [
{
"internalType": "uint256",
"name": "_data",
"type": "uint256"
}
],
"name": "updateData",
"outputs": [],
"stateMutability": "nonpayable",
"type": "function"
}
],
provider
);
resolve({simpleStorage});
return;
}
reject('Provider not recognized');
});
export default getBlockchain;Dependencies Installation
Run:
npm install --save bootstrap
npm install --save ethers@5.4.7
npm install --save @ledgerhq/hw-app-eth
npm install --save @ledgerhq/hw-transport-web-ble
npm install --save buffer
npm install --save next| Package | What does it do? |
|---|---|
| bootstrap (opens in a new tab) | It allows you to use the Bootstrap CSS framework. |
| ethers (opens in a new tab) | It provides you with all the methods to interact with the Ethereum blockchain. For this tutorial, we use the 5.4.7 version. |
| @ledgerhq/hw-app-eth (opens in a new tab) | It will help you ask your Nano to access the ethereum address. |
| @ledgerhq/hw-transport-web-ble (opens in a new tab) | It provides you with all the methods to interact with your Ledger Nano X with a Bluetooth connexion. |
| buffer (opens in a new tab) | The goal is to provide an API that is 100% identical to node's Buffer API. |
Package.json Dependencies
Now that the dependencies are installed you can find them in the "package.js". This is how your "package.json" shoud look like:
{
"name": "e2e-tutorial-contract",
"version": "0.1.0",
"private": true,
"dependencies": {
"@ledgerhq/hw-app-eth": "^6.35.6",
"@ledgerhq/hw-transport-web-ble": "^6.28.4",
"@testing-library/jest-dom": "^5.17.0",
"@testing-library/react": "^13.4.0",
"@testing-library/user-event": "^13.5.0",
"bootstrap": "^5.3.3",
"buffer": "^6.0.3",
"eip55": "^2.1.1",
"ethers": "^5.4.7",
"next": "^14.1.3",
"react": "^18.2.0",
"react-dom": "^18.2.0",
"react-scripts": "5.0.1",
"web-vitals": "^2.1.4"
},
"scripts": {
"build": "next build",
"dev": "next dev",
"start": "next start"
},
"eslintConfig": {
"extends": [
"react-app",
"react-app/jest"
]
},
"browserslist": {
"production": [
">0.2%",
"not dead",
"not op_mini all"
],
"development": [
"last 1 chrome version",
"last 1 firefox version",
"last 1 safari version"
]
}
}Web App Test
Start the Development Server
Run:
npm run devAll the browser do not support the Bluetooth please look at the browser support .
Now the application is up and running. Open the browser and go to localhost:3000, it will display :
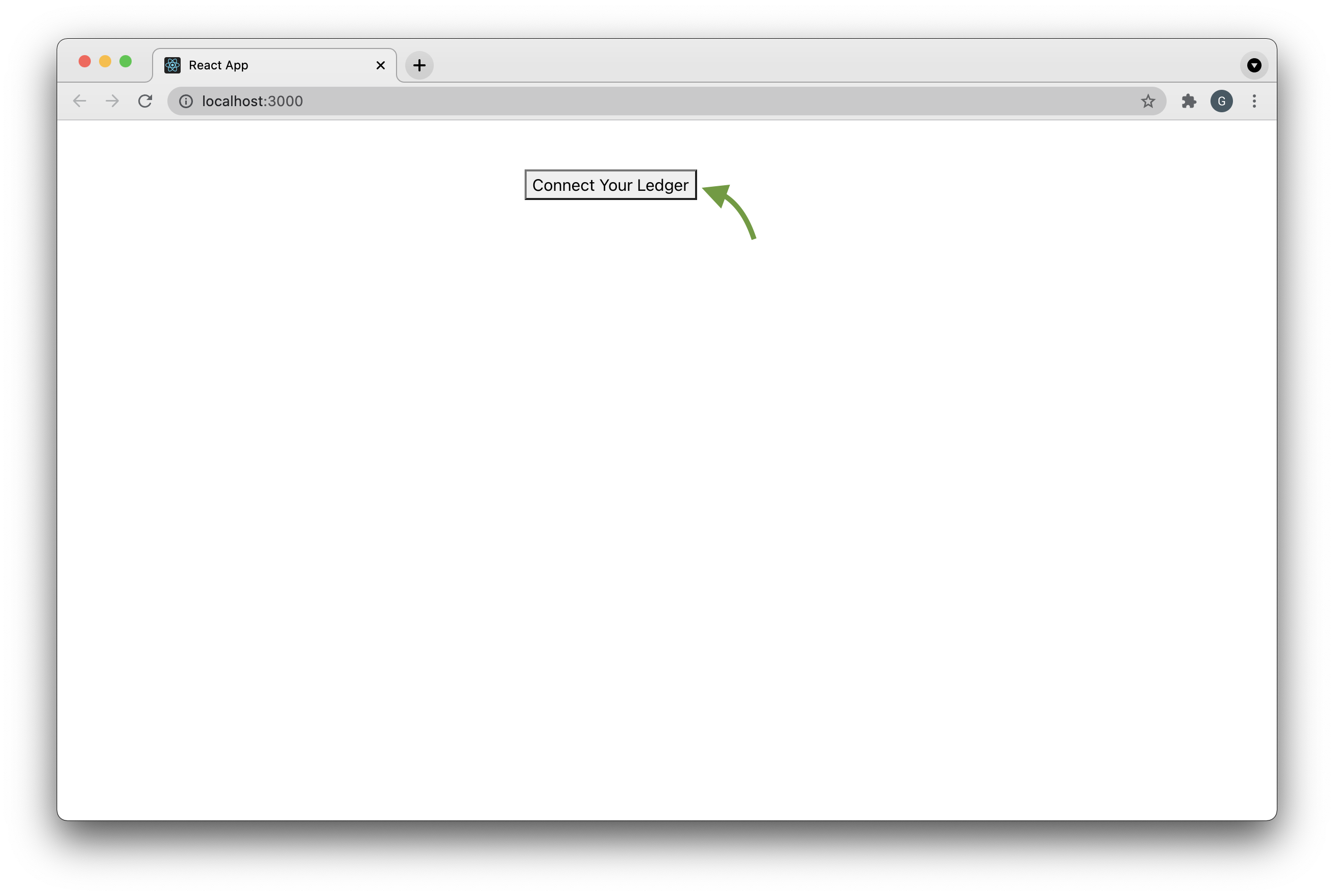 Fig. 2: Application Running on Browser
Fig. 2: Application Running on Browser
Don't click on the button yet.
Launch the Ethereum App
Before clicking on the button, unlock your Nano X and run the Ethereum application. The steps are described below.



For the tutorial to work, go to the Ethereum app settings and enable Blind Signing.
Connect Your Nano to the Application
Now you can click on the button and a popup opens. Choose your Ledger Nano X and click connexion.
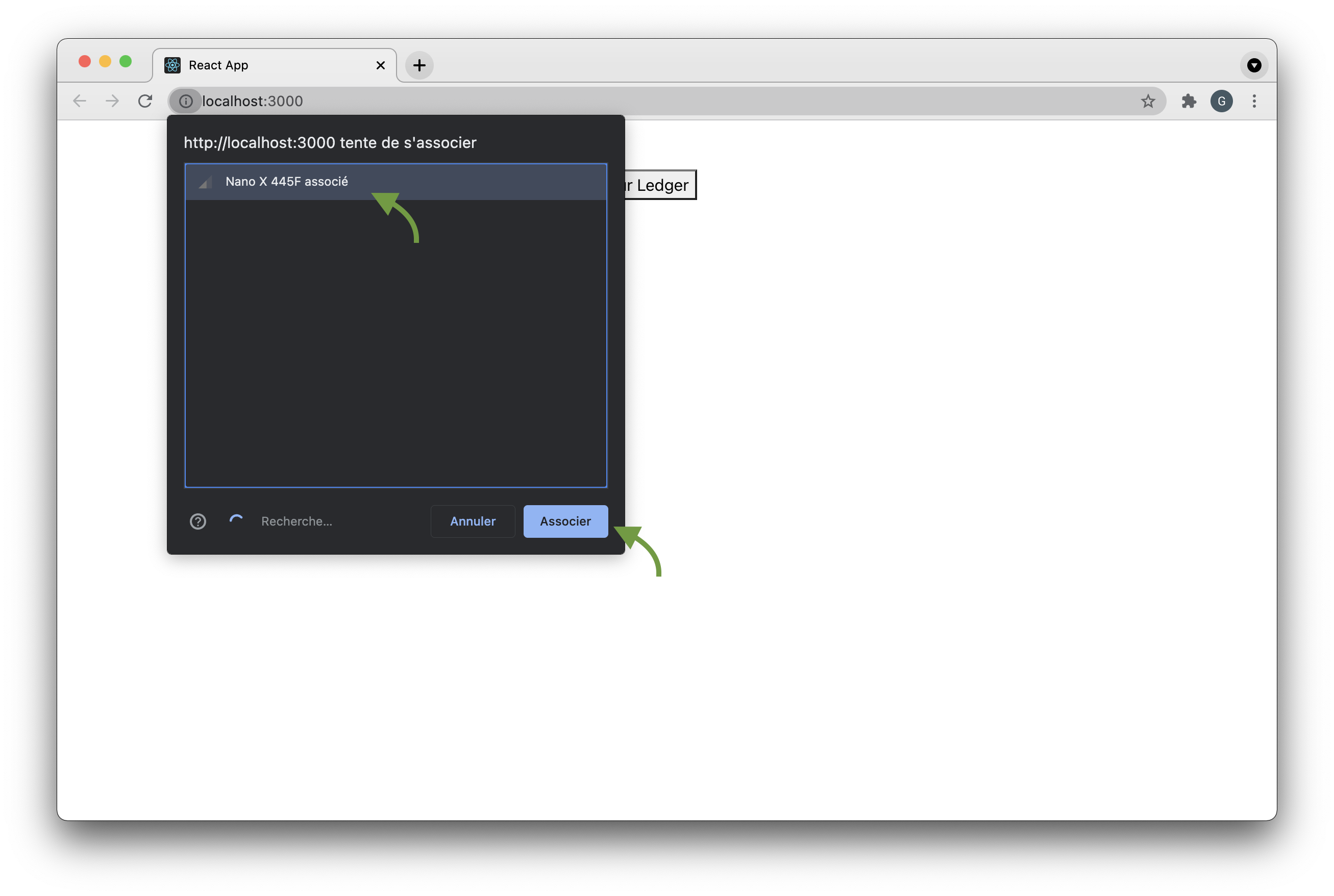 Fig. 6: Connect the Ledger with Bluetooth
Fig. 6: Connect the Ledger with Bluetooth
Read the data of a Smart Contract
Now you can click on the button "Get Data" to read the data of the smart contract. Then the data will be displayed on the screen.
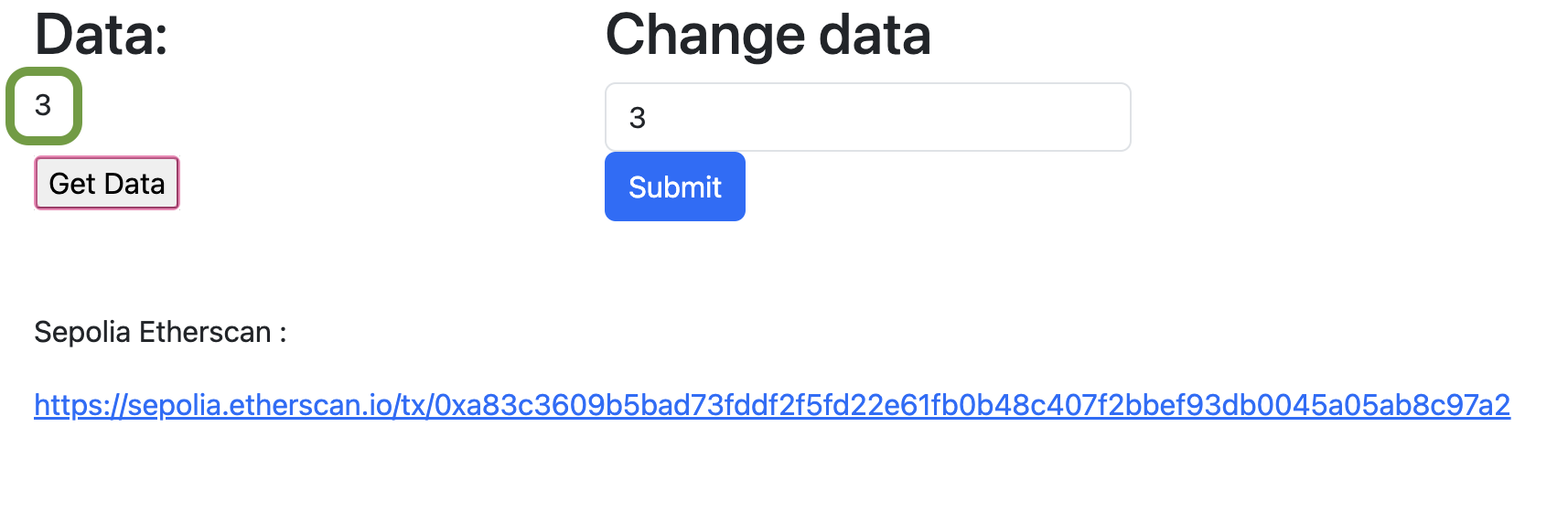 Fig. 7: Get data from a smart contract
Fig. 7: Get data from a smart contract
Update the data of a Smart Contract
Now instead of reading data, we will overwrite the data by calling a function of the smart contract which is "UpdateData".
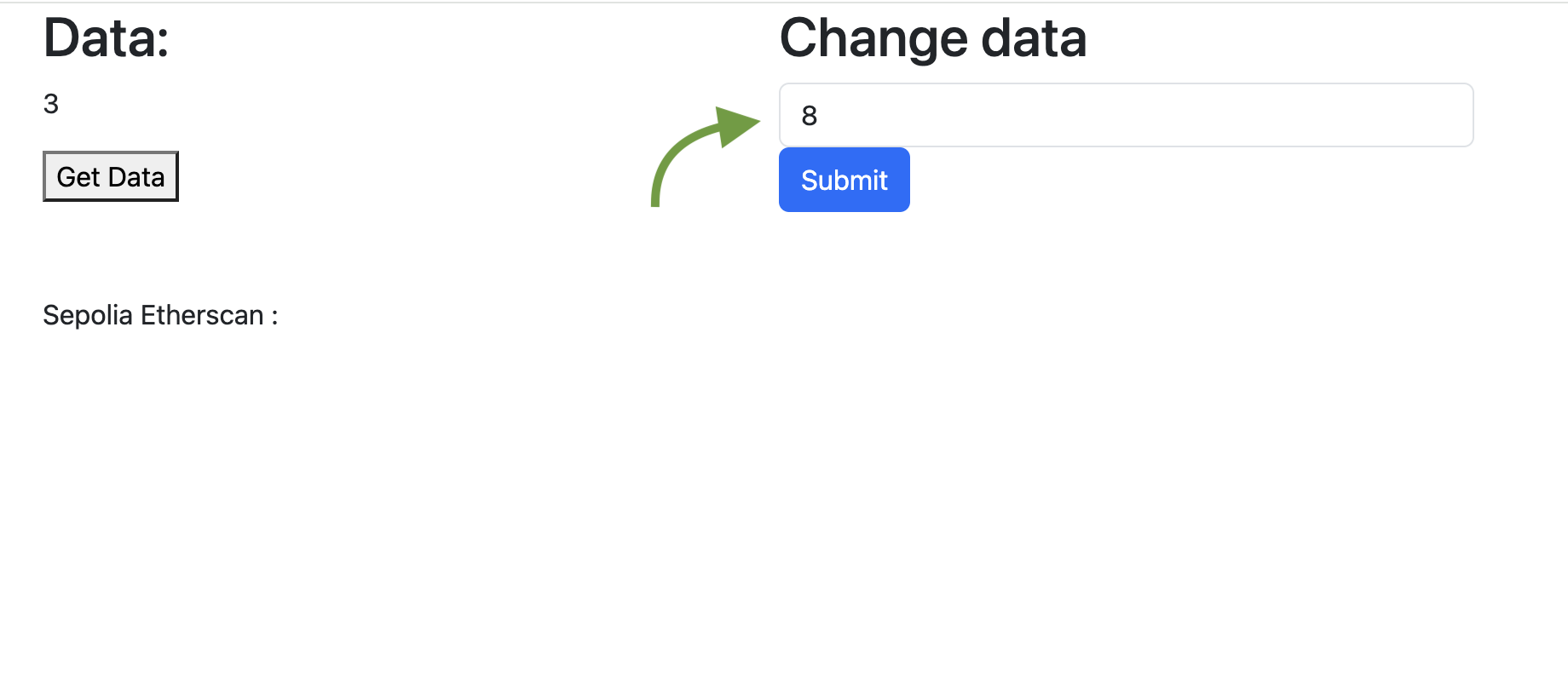 Fig. 8: Change data from a smart contract
Fig. 8: Change data from a smart contract
Verify the Address on your Nano
For security reasons, the address will also be displayed on your Ledger Nano X to verify and confirm the address.







For the Smart Contract call you need to allow blind signing because the smart contract that is called in the tutorial is not yet verified and reviewed by Ledger. But if the smart contract you are calling is accepted by Ledger do not enable blind signing. Moreover, we do not recommend enabling blind signing in other situations as the main purpose to sign with Ledger is the 'Sign what you see' system. And by enabling blind signing it can not ensure that what you see is what you get.
Review the Transaction on Sepolia Etherscan
By updating the data a transaction is created to change this data, it can be verified on Sepolia Etherscan.
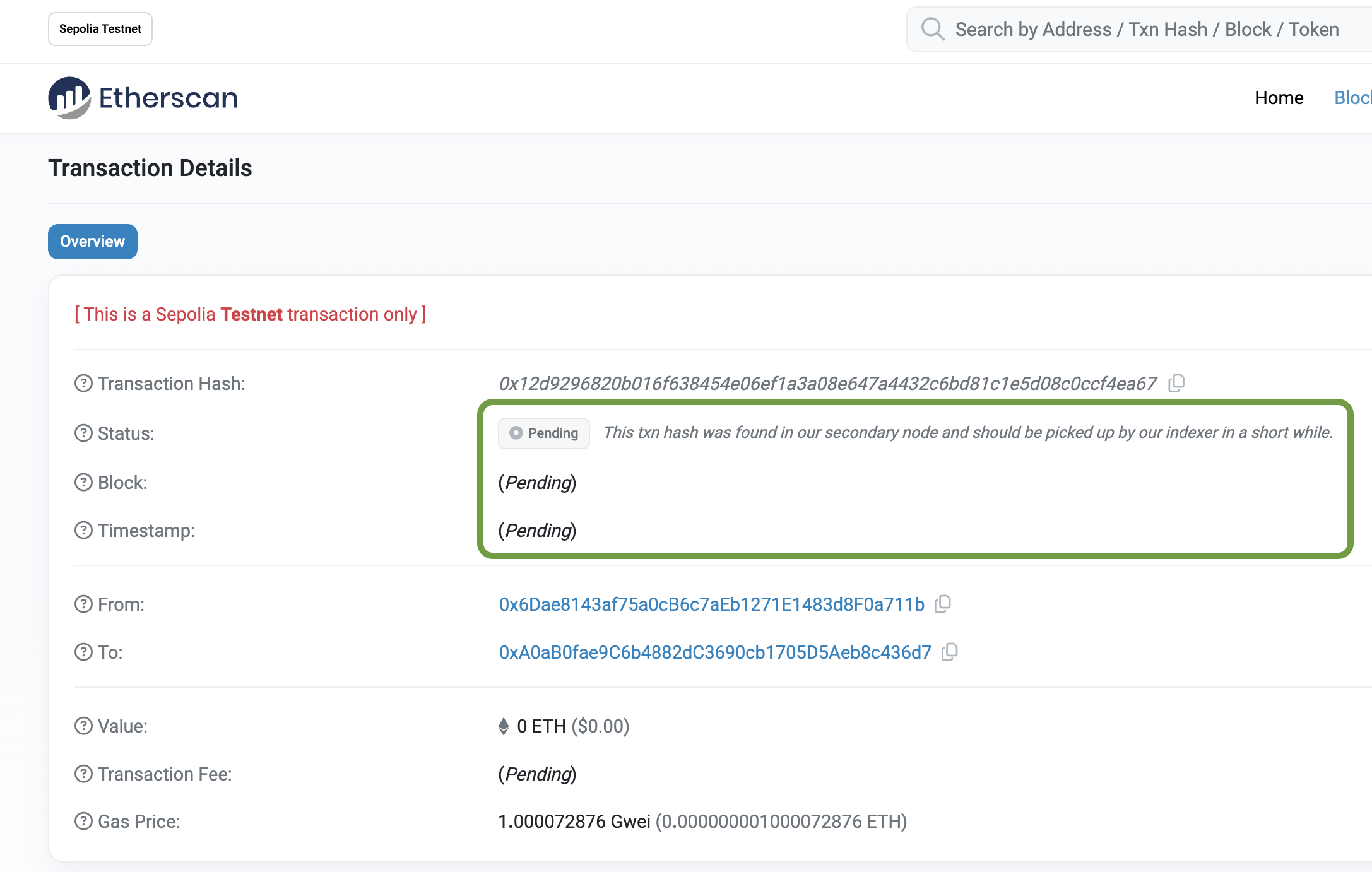
Fig. 15: Sepolia Etherscan
Wait till the status passes to Success.
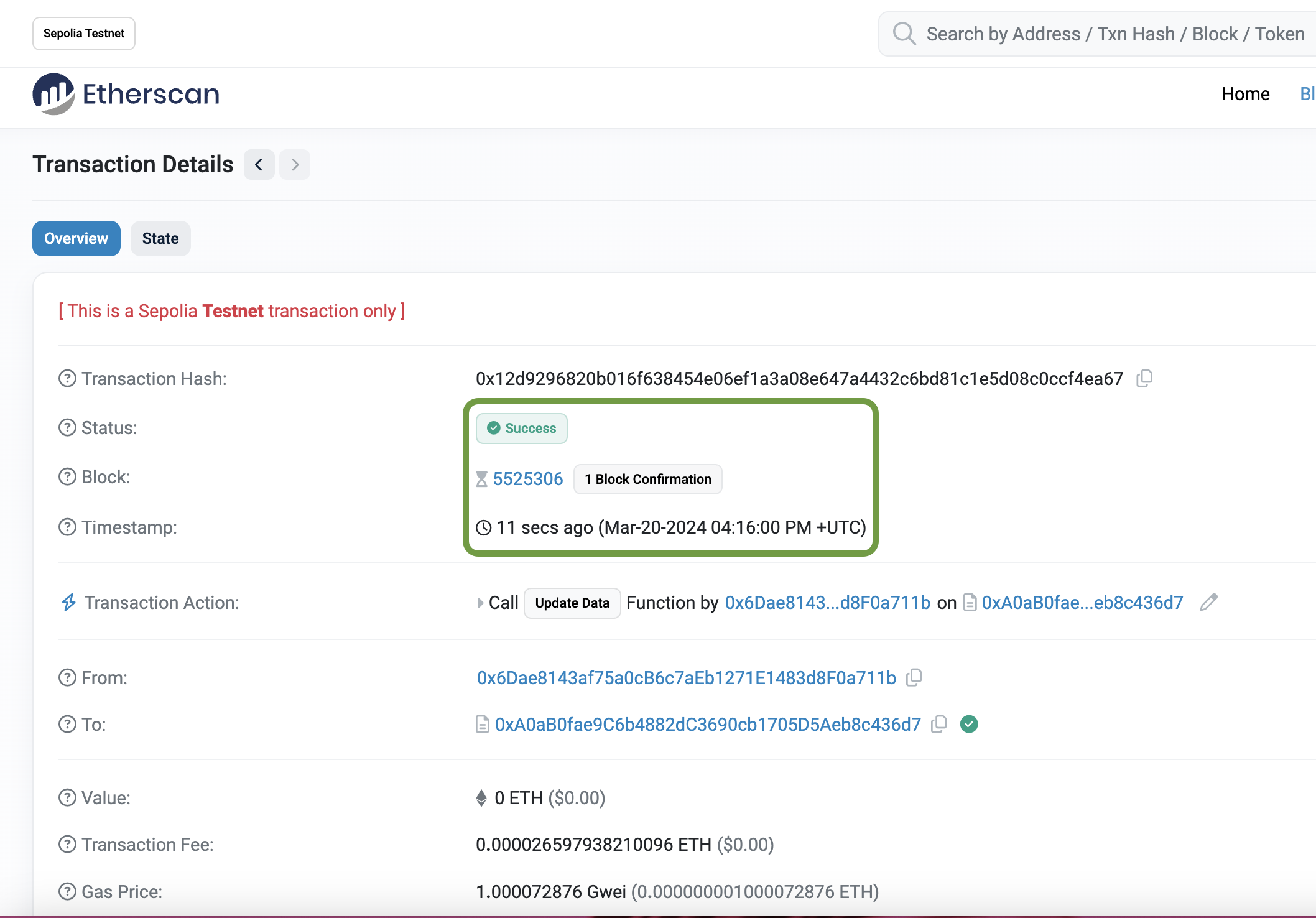
Fig. 16: Sepolia Etherscan
Verify the update of data
Finally, to verify if data was updated, open the web application and click on "Get data".
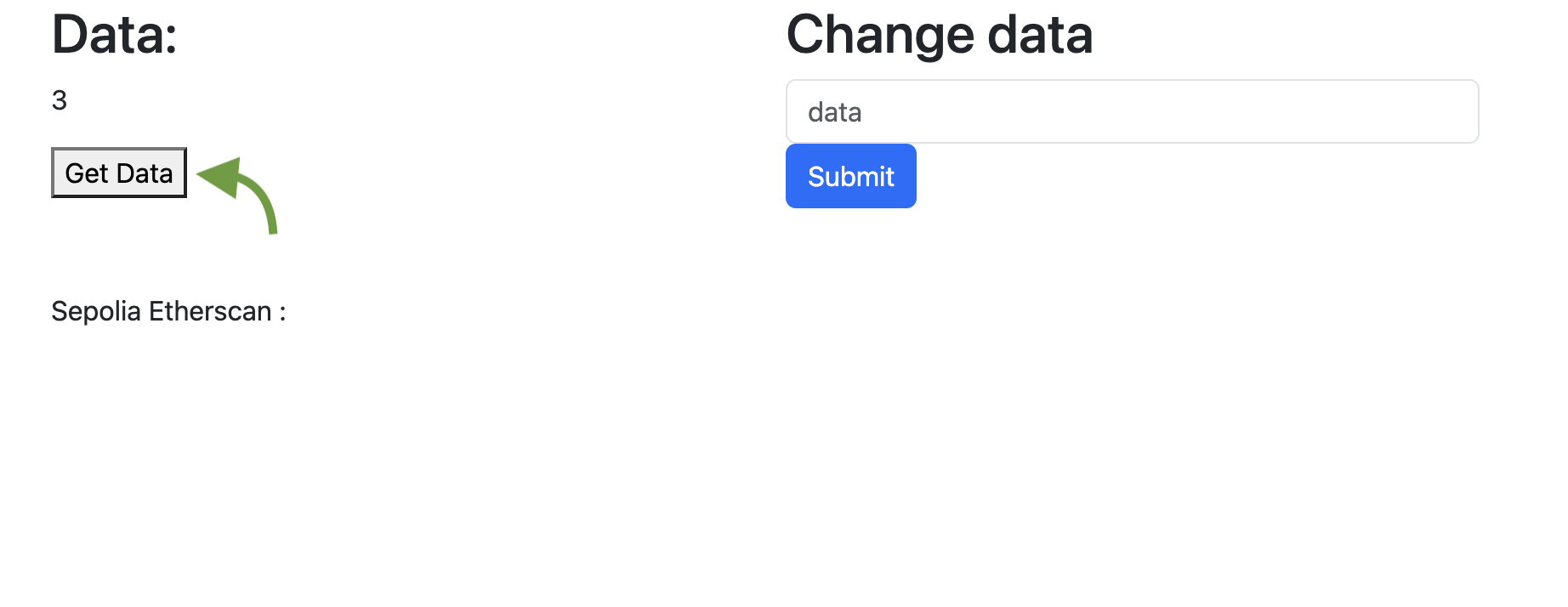
Fig. 17: Verify the data
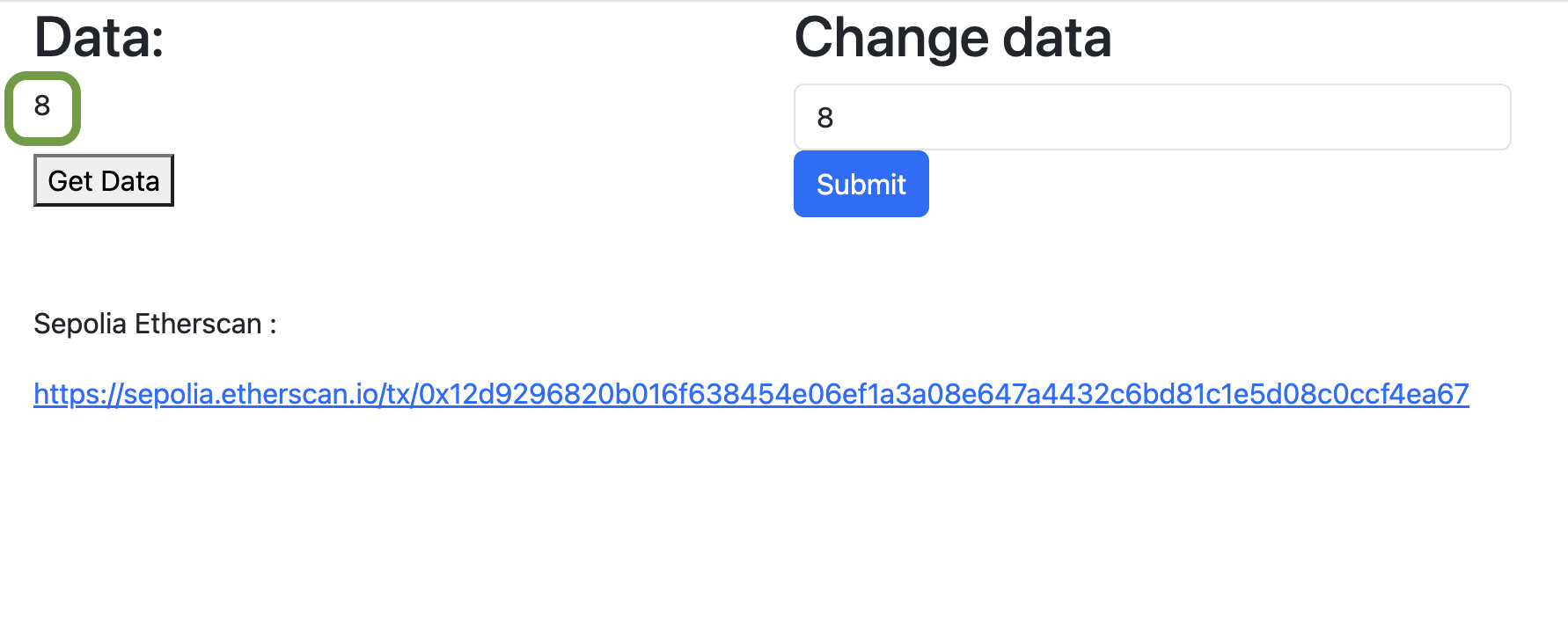
Fig. 18: Verify the data
Congratulations, you have successfully built your first application connected with Ledger!