Security
Application parameters: minimal and declared
Refer to this section for further information.
App permissions
Every app must declare a set of permissions it needs to run properly. These permissions must be minimal, and be declared not only in each app repository, but also listed in the Ledger app database.
The coherence between these permissions and the app Makefile is verified as part of
Ledger guidelines enforcer GitHub workflow,
which is also a requirement.
Ledger will not deploy an app if its permissions have not been registered in Ledger app database.
Derivation path
The application derivation paths must be restricted to coin-specific BIP32 prefix, and declared in the Ledger app database.
The coherence between these derivation path and the app Makefile is verified as part of
Ledger guidelines enforcer GitHub workflow,
which is also a requirement.
More information regarding how to choose and configure derivation paths are available on the application permissions page.
Ledger will not deploy an app if its derivation paths have not been registered in Ledger app database.
Ledger will not deploy apps whose BIP32 prefixes have not been properly set.
If your application derives keys on the hardened path 44’/60’ then the chainID parameter must be different from 0 or 1. This is necessary to avoid replaying transactions broadcoast on Ethereum-like chains on Ethereum. As a general recommendation, and to ensure a good level of privacy for the end user, we recommend to always use the correct coin type in the derivation path as defined in slip44
Signing settings
Signing
All signing transactions/messages action must ask for the user approval before happening.
More information here.
Blind Signing
As a general rule, blind signing should be avoided, however it is tolerated under some circumstances.
For every transaction, the users must be able to verify on the device the amount being transferred and the destination address or the validator/nominator address(es) in the case of a staking operation, and the fees being paid.
When the display of those parameters (Token, smart contract management) is not possible, the transaction should be rejected by the device unless the user has acknowledged that they will be blind signing.
To implement this requirement it is recommended to have a setting menu with the possibility to enable/disable blind signing.
If blind signing is implemented, it must be disabled by default.
You can find implementation example inside Ethereum code base.
CodeQL
CodeQL is required to perform security checks and detect vulnerabilities.
It can be directly integrated into your project by creating a new YAML file: .github/workflows/codeql-workflow.yaml in your repository.
A complete codeql-workflow.yml file is available in the repository of the Boilerplate app.
The first part of the file is an initialization of what is needed to build your Ledger app and a declaration of languages used in your code so CodeQL analyzes it in the right way.
jobs:
analyse:
name: Analyse
strategy:
matrix:
sdk: ["$NANOX_SDK", "$NANOSP_SDK", "$STAX_SDK", "$FLEX_SDK"]
language: [ 'cpp' ]
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
container:
image: ghcr.io/ledgerhq/ledger-app-builder/ledger-app-builder-legacy:liteThe action part needs 4 steps:
- Clone your repository
- Initialize CodeQL:
- Declaration of which languages are used and the chosen queries. Please choose the
security-and-qualityqueries.
- Declaration of which languages are used and the chosen queries. Please choose the
- Build the app. Be careful : the initialization of CodeQL needs to be done before building the app so that CodeQL makes the code dictionary during the building stage.
- Perform the CodeQL analysis
steps:
- name: Clone
uses: actions/checkout@v4
with:
submodules: true
- name: Initialize CodeQL
uses: github/codeql-action/init@v3
with:
languages: ${{ matrix.language }}
queries: security-and-quality
- name: Build
run: |
make BOLOS_SDK=${{ matrix.sdk }}
- name: Perform CodeQL Analysis
uses: github/codeql-action/analyze@v3Next the results of CodeQL are displayed on your GitHub security view, in the “Code scanning alerts” panel. If CodeQL is configured to run when a pull request (PR) on some branches is made, the results will also be shown in the “Checks” parts of the PR.
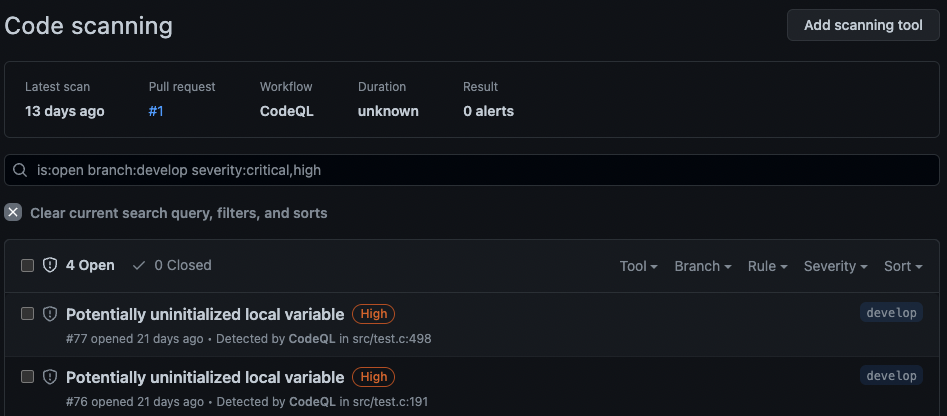
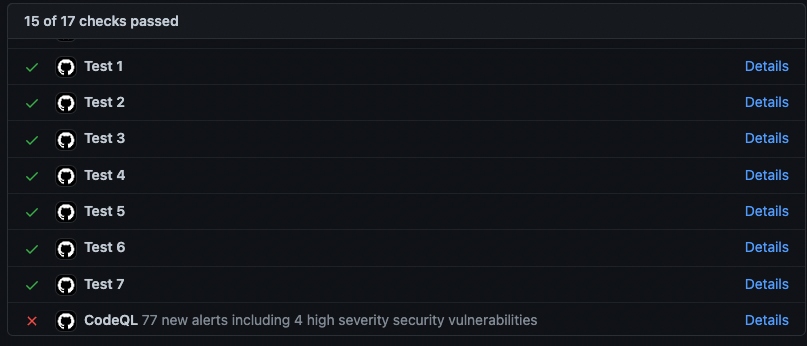
The security issues with a severity level higher than low must be fixed before going through the security audit. The quality issues with a level set to error must also be fixed.