React Native Bluetooth on Android (Nano X only)
Introduction
In this section you will see how to create a React Native application using the @ledgerhq/react-native-hw-transport-ble. For this project some general prerequisites are mandatory and you can find them here.
Then you can now go through the prerequisite for Android development below.
One-time setup
Environnement
Make sure you go through:
- the prerequisites.
- the Mobile Environment Setup.
Environnement variables
If you are using bash, put the environment variable into the bash_profile as below:
cd ~/
touch ~/.bash_profile;
open -e .bash_profileexport ANDROID_HOME=$HOME/Library/Android/sdk
export PATH=$PATH:$ANDROID_HOME/emulator
export PATH=$PATH:$ANDROID_HOME/tools
export PATH=$PATH:$ANDROID_HOME/tools/bin
export PATH=$PATH:$ANDROID_HOME/platform-toolsDo the same if you are using zsh or anything else. Remember the file will be named differently (eg. zsh => .zprofile)
App Coding
Now that we have set up the prerequisites, you can now create the application. In this integration, we will use the ethereum application.
App setup
First, open a terminal and create a new project. For this tutorial the project will be named “myAndroidBTApp”.
Run:
react-native init myAndroidBTApp
cd myAndroidBTAppThe dependencies of ‘CocoaPods’ may take some time to initialize.
Files
Run:
mkdir src
touch polyfill.js
touch src/DeviceItem.js
touch src/DeviceSelectionScreen.js
touch src/ShowAddressScreen.jspolyfill.js
In “polyfill.js”, copy-paste the following code:
global.Buffer = require("buffer").Buffer;index.js
Then import the “polyfill.js” in “index.js” as shown below:
/**
* @format
*/
import "./polyfill"; //import this
import { AppRegistry } from "react-native";
import App from "./src/App"; //modify this import
import { name as appName } from "./app.json";
AppRegistry.registerComponent(appName, () => App);App.js
Move the file named “App.js” in the “src” folder and copy-paste the following code:
import React, { Component } from "react";
import DeviceSelectionScreen from "./DeviceSelectionScreen";
import ShowAddressScreen from "./ShowAddressScreen";
import TransportBLE from "@ledgerhq/react-native-hw-transport-ble";
// This is helpful if you want to see BLE logs. (only to use in dev mode)
class App extends Component {
state = {
transport: null,
};
onSelectDevice = async (device) => {
const transport = await TransportBLE.open(device);
transport.on("disconnect", () => {
// Intentionally for the sake of simplicity we use a transport local state
// and remove it on disconnect.
// A better way is to pass in the device.id and handle the connection internally.
this.setState({ transport: null });
});
this.setState({ transport });
};
render() {
const { transport } = this.state;
if (!transport) {
return <DeviceSelectionScreen onSelectDevice={this.onSelectDevice} />;
}
return <ShowAddressScreen transport={transport} />;
}
}
export default App;In “DeviceItem.js” copy-paste the following code:
import React, { Component } from "react";
import {
Text,
TouchableOpacity,
StyleSheet,
ActivityIndicator,
} from "react-native";
class DeviceItem extends Component {
state = {
pending: false,
};
onPress = async () => {
this.setState({ pending: true });
try {
await this.props.onSelect(this.props.device);
} finally {
this.setState({ pending: false });
}
};
render() {
const { device } = this.props;
const { pending } = this.state;
return (
<TouchableOpacity
style={styles.deviceItem}
onPress={this.onPress}
disabled={pending}
>
<Text style={styles.deviceName}>{device.name}</Text>
{pending ? <ActivityIndicator /> : null}
</TouchableOpacity>
);
}
}
export default DeviceItem;
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
deviceItem: {
paddingVertical: 16,
paddingHorizontal: 32,
marginVertical: 8,
marginHorizontal: 16,
borderColor: "#ccc",
borderWidth: 1,
flexDirection: "row",
alignItems: "center",
justifyContent: "space-between",
},
deviceName: {
fontSize: 20,
fontWeight: "bold",
},
});In “DeviceSelectionScreen.js” copy-paste the following code:
import React, { Component } from "react";
import {
StyleSheet,
Text,
View,
TouchableOpacity,
FlatList,
Platform,
PermissionsAndroid
} from "react-native";
import { Observable } from "rxjs";
import AppEth from "@ledgerhq/hw-app-eth";
import TransportBLE from "@ledgerhq/react-native-hw-transport-ble";
import QRCode from "react-native-qrcode-svg";
import DeviceItem from "./DeviceItem";
const deviceAddition = device => ({ devices }) => ({
devices: devices.some(i => i.id === device.id)
? devices
: devices.concat(device)
});
class DeviceSelectionScreen extends Component {
state = {
devices: [],
error: null,
refreshing: false
};
async componentDidMount() {
// NB: this is the bare minimal. We recommend to implement a screen to explain to user.
if (Platform.OS === "android") {
await PermissionsAndroid.request(
PermissionsAndroid.PERMISSIONS.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION
);
}
let previousAvailable = false;
new Observable(TransportBLE.observeState).subscribe(e => {
if (e.available !== previousAvailable) {
previousAvailable = e.available;
if (e.available) {
this.reload();
}
}
});
this.startScan();
}
componentWillUnmount() {
if (this.sub) this.sub.unsubscribe();
}
startScan = async () => {
this.setState({ refreshing: true });
this.sub = new Observable(TransportBLE.listen).subscribe({
complete: () => {
this.setState({ refreshing: false });
},
next: e => {
if (e.type === "add") {
this.setState(deviceAddition(e.descriptor));
}
// NB there is no "remove" case in BLE.
},
error: error => {
this.setState({ error, refreshing: false });
}
});
};
reload = async () => {
if (this.sub) this.sub.unsubscribe();
this.setState(
{ devices: [], error: null, refreshing: false },
this.startScan
);
};
keyExtractor = (item: *) => item.id;
onSelectDevice = async device => {
try {
await this.props.onSelectDevice(device);
} catch (error) {
this.setState({ error });
}
};
renderItem = ({ item }: { item: * }) => {
return <DeviceItem device={item} onSelect={this.onSelectDevice} />;
};
ListHeader = () => {
const { error } = this.state;
return error ? (
<View style={styles.header}>
<Text style={styles.headerTitle}>Sorry, an error occured</Text>
<Text style={styles.errorTitle}>{String(error.message)}</Text>
</View>
) : (
<View style={styles.header}>
<Text style={styles.headerTitle}>Scanning for Bluetooth...</Text>
<Text style={styles.headerSubtitle}>
Power up your Ledger Nano X and enter your pin.
</Text>
</View>
);
};
render() {
const { devices, error, refreshing } = this.state;
return (
<FlatList
extraData={error}
style={styles.list}
data={devices}
renderItem={this.renderItem}
keyExtractor={this.keyExtractor}
ListHeaderComponent={this.ListHeader}
onRefresh={this.reload}
refreshing={refreshing}
/>
);
}
}
export default DeviceSelectionScreen;
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
header: {
paddingTop: 80,
paddingBottom: 36,
alignItems: "center"
},
headerTitle: {
fontSize: 22,
marginBottom: 16
},
headerSubtitle: {
fontSize: 12,
color: "#999"
},
list: {
flex: 1
},
errorTitle: {
color: "#c00",
fontSize: 16,
marginBottom: 16
}
});In “ShowAddressScreen.js” copy-paste the following code:
import React, { Component } from "react";
import { StyleSheet, Text, View } from "react-native";
import AppEth from "@ledgerhq/hw-app-eth";
import TransportBLE from "@ledgerhq/react-native-hw-transport-ble";
import QRCode from "react-native-qrcode-svg";
const delay = (ms) => new Promise((success) => setTimeout(success, ms));
class ShowAddressScreen extends Component {
state = {
error: null,
address: null,
};
async componentDidMount() {
while (!this.state.address) {
if (this.unmounted) return;
await this.fetchAddress(false);
await delay(500);
}
await this.fetchAddress(true);
}
async componentWillUnmount() {
this.unmounted = true;
}
fetchAddress = async (verify) => {
const { transport } = this.props;
try {
const eth = new AppEth(transport);
const path = "44'/60'/0'/0/0"; // HD derivation path
const { address } = await eth.getAddress(path, verify);
if (this.unmounted) return;
this.setState({ address });
} catch (error) {
// in this case, user is likely not on Ethereum app
if (this.unmounted) return;
this.setState({ error });
return null;
}
};
render() {
const { address, error } = this.state;
return (
<View style={styles.ShowAddressScreen}>
{!address ? (
<>
<Text style={styles.loading}>Loading your Ethereum address...</Text>
{error ? (
<Text style={styles.error}>
A problem occurred, make sure to open the Ethereum application
on your Ledger Nano X. (
{String((error && error.message) || error)})
</Text>
) : null}
</>
) : (
<>
<Text style={styles.title}>Ledger Live Ethereum Account 1</Text>
<QRCode value={address} size={300} />
<Text style={styles.address}>{address}</Text>
</>
)}
</View>
);
}
}
export default ShowAddressScreen;
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
ShowAddressScreen: {
flex: 1,
padding: 16,
alignItems: "center",
justifyContent: "center",
},
error: {
color: "#c00",
fontSize: 16,
},
loading: {
color: "#999",
fontSize: 16,
},
title: {
fontSize: 22,
marginBottom: 16,
},
address: {
marginTop: 16,
color: "#555",
fontSize: 14,
},
});The folder will contain these files:
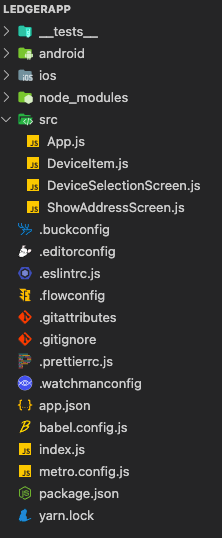 Fig. 4: Folder of the Application
Fig. 4: Folder of the Application
Dependencies
Installation
Run:
npm install --save react-native-qrcode-svg
npm install --save react-native-svg
npm install --save rxjs
npm install --save @ledgerhq/react-native-hw-transport-ble
npm install --save react-native-ble-plx
npx react-native link react-native-ble-plx
npm install --save buffer
npm install --save @ledgerhq/hw-app-eth| Package | What it does |
|---|---|
| react-native-qrcode-svg | It allows you to create a QR code. |
| react-native-svg | It is a mandatory package to use react-native-qrcode-svg |
| rxjs | It is a rewrite of “Reactive-Extensions/RxJS” and is the latest production-ready version of RxJS. |
| @ledgerhq/hw-transport-web-ble | It provides you with all the methods to interact with your Ledger Nano X with a Bluetooth connexion. |
| react-native-ble-plx | It scans the bluetooth devices. |
| buffer | The goal is to provide an API that is 100% identical to node’s Buffer API. |
| hw-app-eth | It helps you ask your Ledger device to access the ethereum address. |
package.json
Now that the dependencies are installed you can find them in the “package.js”. This is how your “package.json” has to look like.
{
"name": "myAndroidBTApp",
"version": "0.0.1",
"private": true,
"scripts": {
"android": "react-native run-android",
"ios": "react-native run-ios",
"start": "react-native start",
"test": "jest",
"lint": "eslint ."
},
"dependencies": {
"@ledgerhq/hw-app-eth": "^6.16.2",
"@ledgerhq/react-native-hw-transport-ble": "^6.15.0",
"buffer": "^6.0.3",
"react": "17.0.2",
"react-native": "0.66.3",
"react-native-ble-plx": "^2.0.3",
"react-native-qrcode-svg": "^6.1.1",
"react-native-svg": "^12.1.1",
"rxjs": "^7.4.0"
},
"devDependencies": {
"@babel/core": "^7.16.0",
"@babel/runtime": "^7.16.3",
"@react-native-community/eslint-config": "^3.0.1",
"babel-jest": "^27.3.1",
"eslint": "^8.3.0",
"jest": "^27.3.1",
"metro-react-native-babel-preset": "^0.66.2",
"react-test-renderer": "17.0.2"
},
"jest": {
"preset": "react-native"
}
}
Build.gradle Modification
In “build.gradle”, in the “android” folder change minSdkVersion = 21 to minSdkVersion = 24.
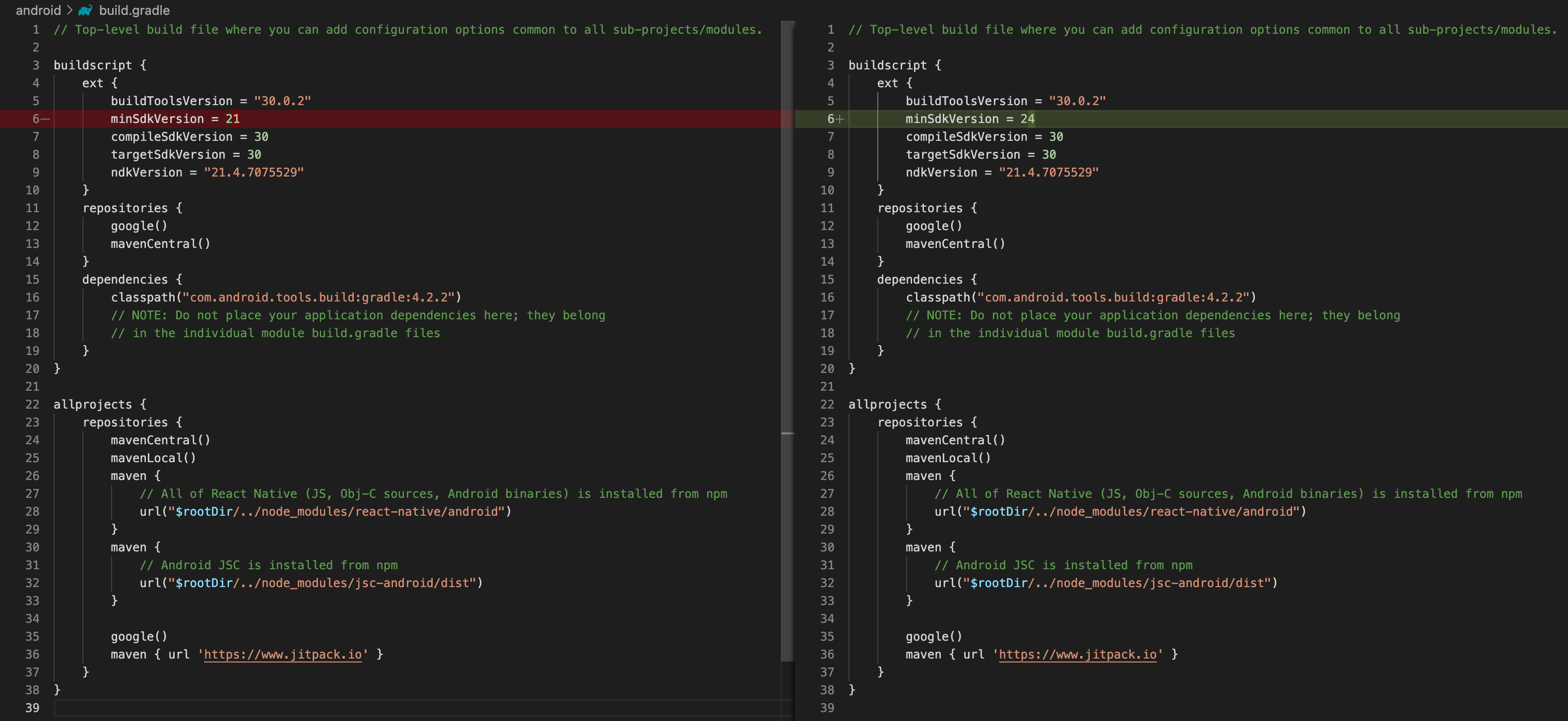 Fig. 5: Build.gradle Modify the minSdkVersion
Fig. 5: Build.gradle Modify the minSdkVersion
You can now test the application you have built.
App Launch
App testing is done on your smartphone because the Android Studio emulator cannot use Bluetooth or USB connexions.
Please refer to the information for Android Emulator Limitation.
Enable Developer Settings
To integrate an application on your Android smartphone you have to enable the developer role. To do that go to Settings > About Phone > Build Number, and tap 7 times on build number to enable the developer settings.
Then go to Settings > System > Advanced > Developer Options and enable the “USB debugging” as well as “Install via USB”
Connect your phone to your computer, and run the command below to check your device is connected:
adb devicesIf all goes well, the list of devices is displayed as shown below:
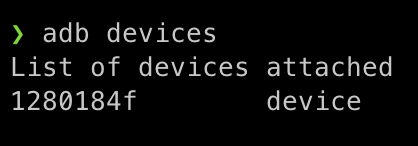
For more information about enabling the developer settings on your android device go to android studio docs.
Start the Development Server
You can now open a terminal, go to the “myAndroidBTApp” folder, and start the server by running:
npm startInstall the App on Device
Keep the terminal where “metro” is running open and open a new terminal. In this new terminal go to your app folder:
cd myAndroidBTAppRun the command below to install the application on your android device. It assumes your smartphone is connected and your device is recognized by the command adb devices as mentioned in the Previous Step.
npm run androidA window will pop up on your android device to install the application. Click on “Yes” to install it and run it.
Launching the App
When launching the application it will be displayed as the image below. You must have the Bluetooth and location activated.

If this is not what you see, you may get:

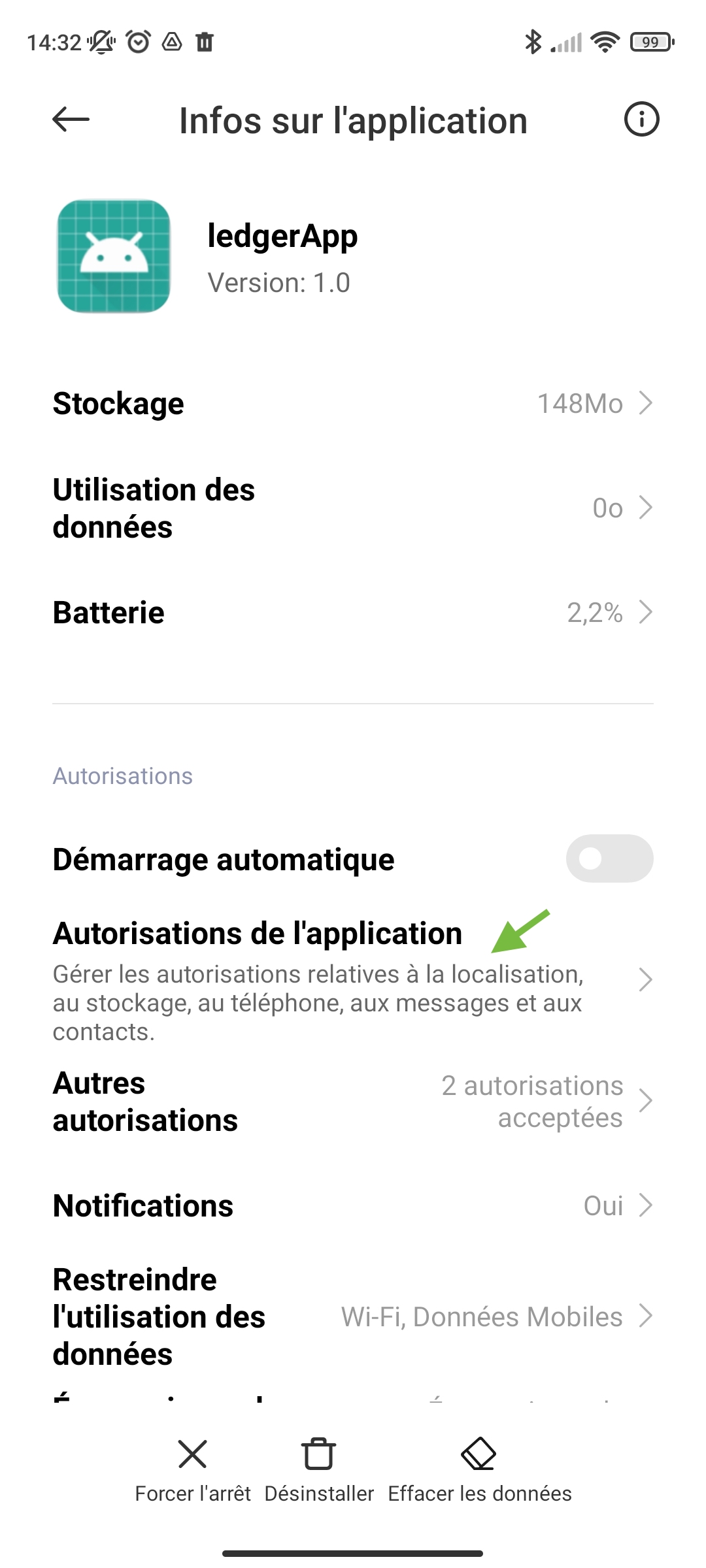
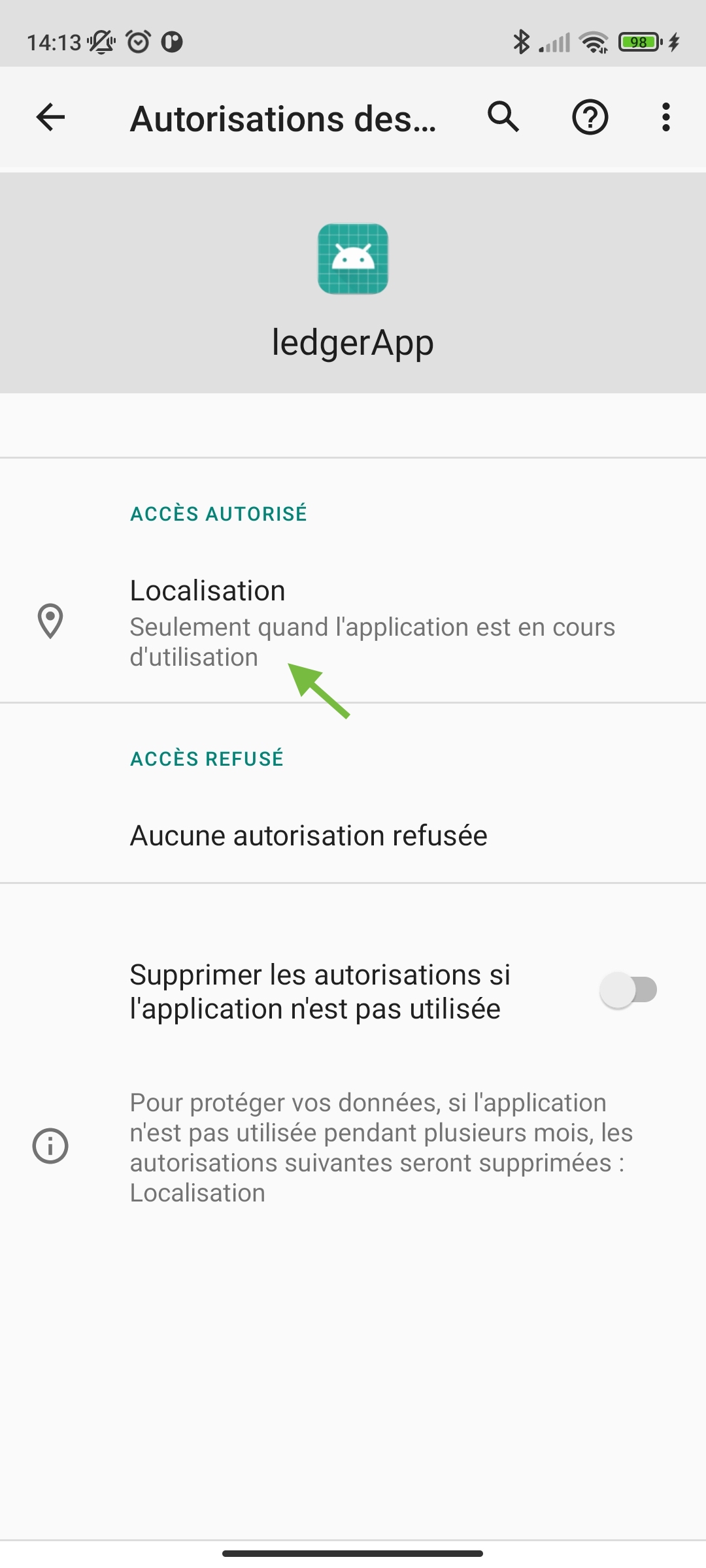
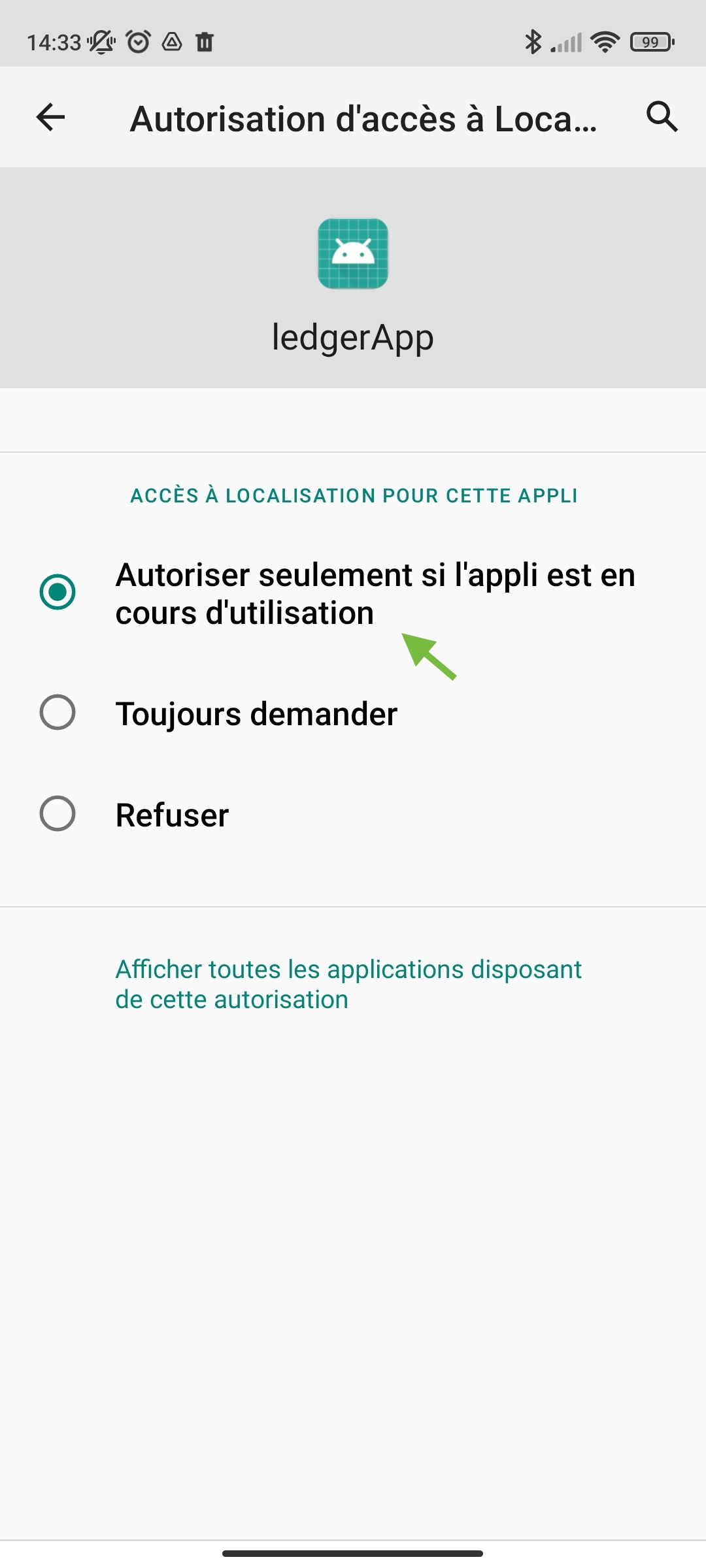
For more information about enabling the Bluetooth settings on your android device go to the troubleshooting tab.
Pairing the Ledger Nano X
To pair your Ledger Nano X, unlock it.

Now try to pair the Ledger Nano X to your android smartphone.
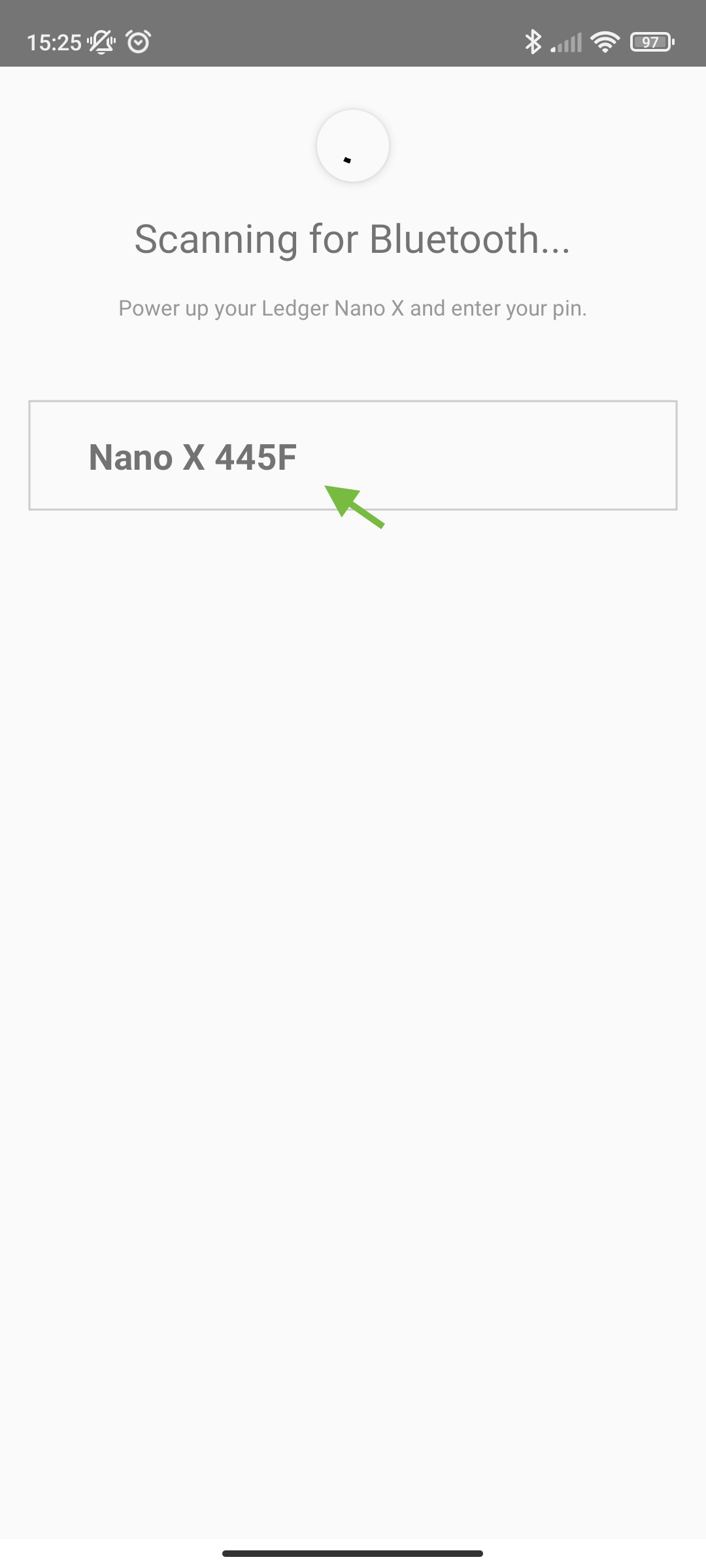
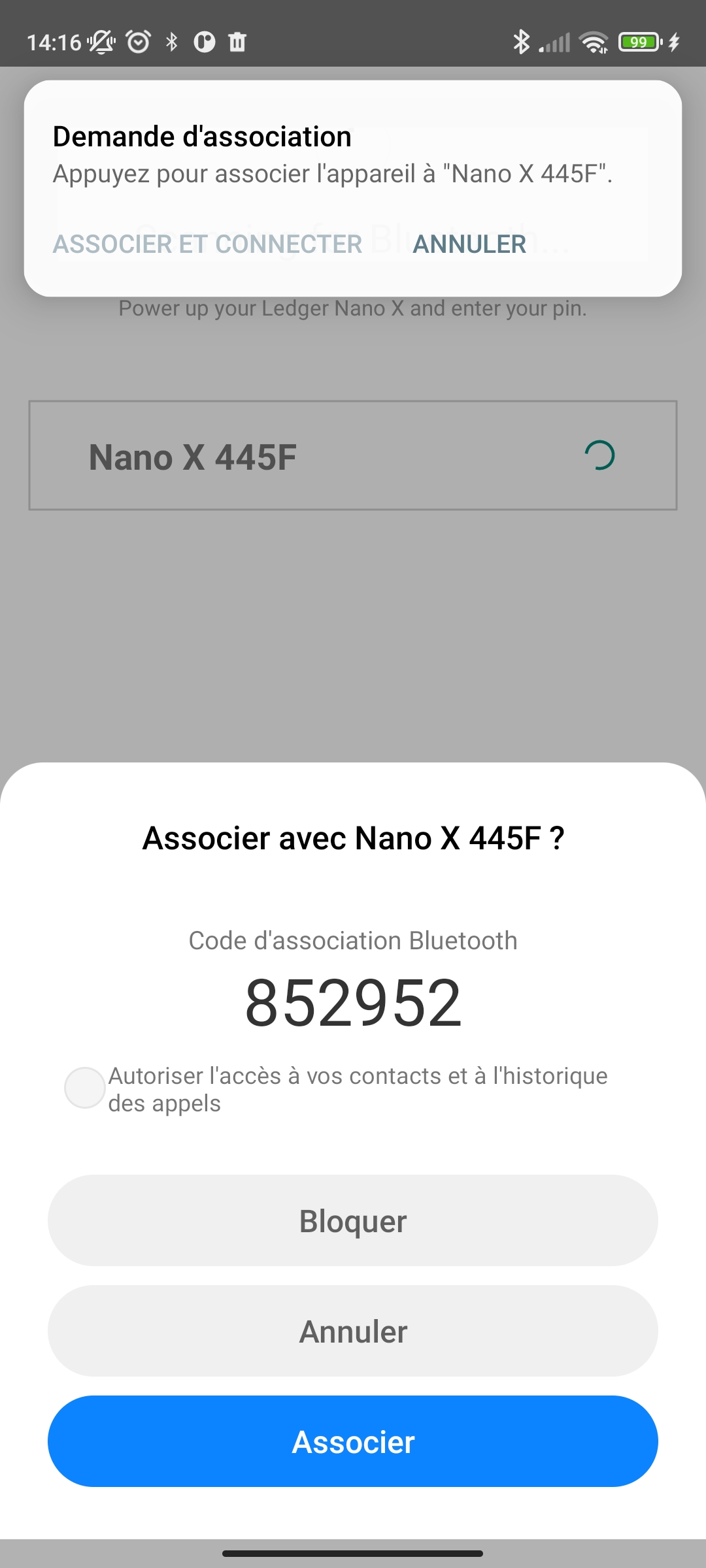
Pairing and Launching the Ethereum App on Nano X
When pairing, the pairing code will be displayed on your Ledger Nano X to confirm.



Now that the pairing is complete, the Nano X is ready with the ethereum application. If all goes well you see the address of your ethereum account displayed.
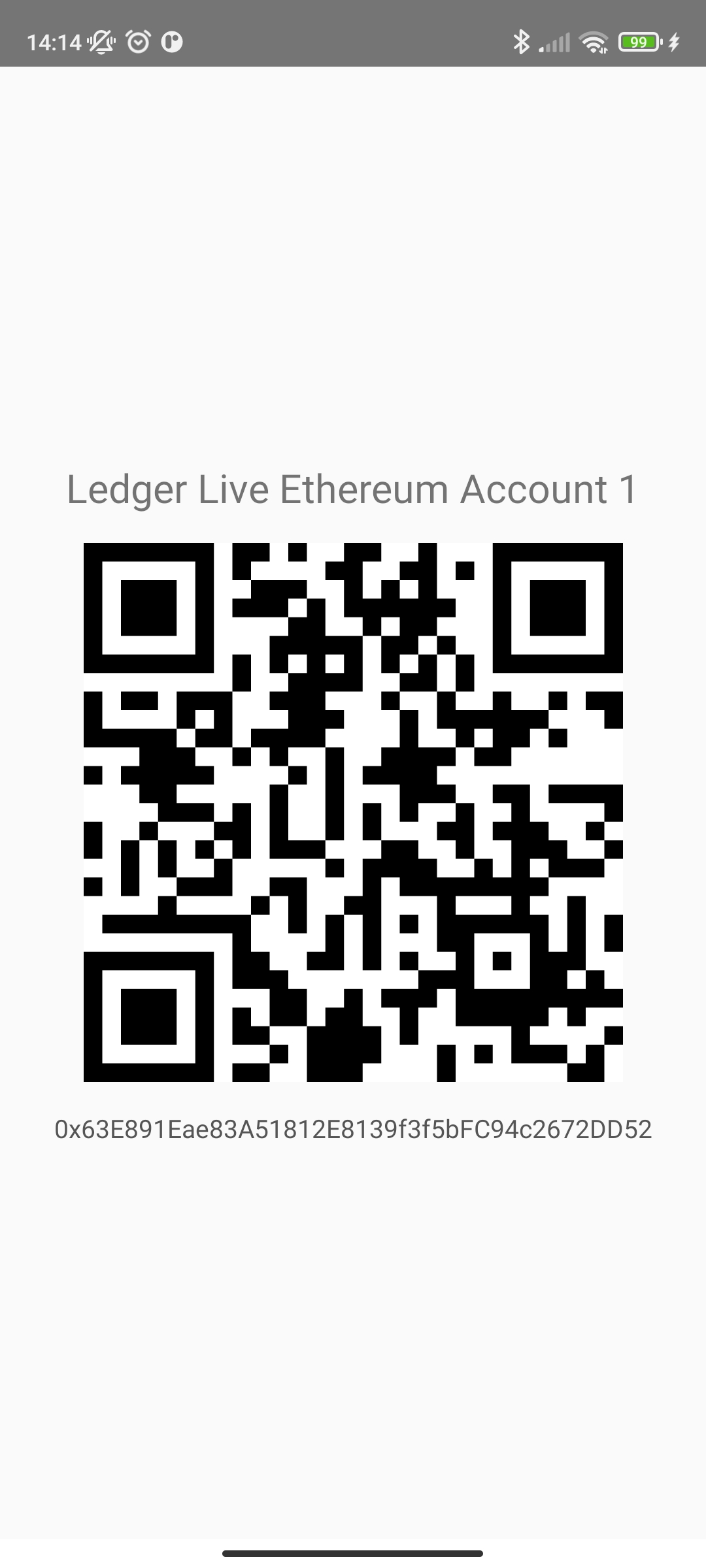
Verify the Address
For security purposes, we display on your Nano X the same ethereum address for you to confirm.



Congratulations you have successfully built your first Android Bluetooth application connected to your Ledger!