Clear Signing Overview
Every day, millions of users blindly approve transactions they can’t read. Clear Signing transforms this incomprehensible hex data into plain language that anyone can verify.
The Problem: Blind Signing
When using traditional blockchain wallets, users face a critical security challenge: blind signing. They’re presented with unreadable transaction hashes or encoded data, making it impossible to verify what they’re actually authorizing.

- •Shows only incomprehensible transaction hashes
- •Cannot verify transaction content or recipient
- •High risk of scams and phishing attacks
- •Poor user experience leads to mistakes
0x23b872dd00000000000000000000000…
- •Shows formatted, readable transaction details
- •Verifies recipient, amount, and function
- •Reduces risk through complete transparency
- •Improves confidence and understanding
Maximum slippage: 0.5%
The Solution: Clear Signing
Clear Signing is an open standard that makes blockchain transactions readable. Instead of showing users cryptic hex strings, it displays exactly what will happen: “Send 100 USDC to alice.eth” or “Swap 1 ETH for 2,500 USDC on Uniswap.”
As a developer, you make this possible by creating a simple metadata file that describes your smart contract’s functions. Once submitted and reviewed, every transaction through your protocol becomes instantly understandable, protecting users and building trust.
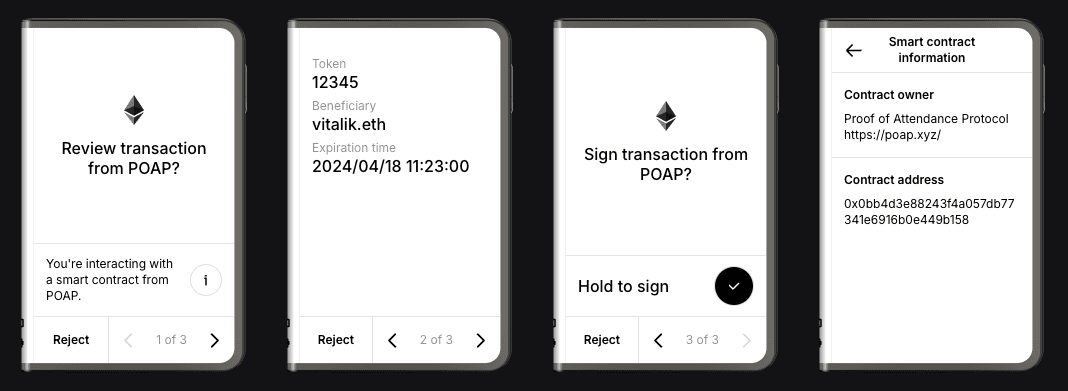
Example: A POAP claim transaction displayed with Clear Signing on Ledger Stax
Real-World Examples
0x23b872dd000000000000000000000000…
000000000000000000000000a0b86991…
000000000000000000000000000001f4
Why It Matters
How It Works
Create Metadata
Write a JSON file that describes your smart contract functions in human-readable terms.
Submit for Review
Open a pull request to the Clear Signing Registry.
Automatic Integration
Compatible wallets automatically fetch your metadata and display transactions in plain language.
Users Benefit
Users see exactly what they’re signing, building trust and preventing mistakes.
Built on Open Standards
Clear Signing implements ERC-7730, an Ethereum Improvement Proposal that standardizes human-readable transaction signing across the entire ecosystem.
Security Guarantee: Clear Signing never modifies transaction data. It only adds a display layer while maintaining complete blockchain security through verified metadata, required user approval, and open source transparency.
Ready to Protect Your Users?
Clear Signing is already protecting millions of users in Ledger Wallet and partner wallets. Join the growing ecosystem of protocols making blockchain safer and more accessible for everyone.